How Significant is “RTMP Ingest” to the Live Streaming Landscape?

Live streams have taken the world by storm. Across industries, the utilization of live streams spans beyond conventional purposes with the revenue projected to peak at $70 billion by 2021.
The scope of real-time video delivery and distribution is so colossal that broadcasters have begun taking advantage of this powerful technology to reach the masses, giving them live coverage of the happening.
And among the backend tech stack that is involved in helping audiences get close to the real-life experience of the virtual event on their gadgets lies RTMP.
Table of Contents
Basics of RTMP
RTMP or the “Real-Time Messaging Protocol” is a significant delivery method for the seamless functioning of live streaming. It also plays a major role in the OTT platform for delivering the video content from an encoder to the host. Developed based on TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), RTMP was initially designed to work in conjunction with the Adobe Flash Player.
To put it simply, RTMP is a pathway that connects the host server and video player to transmit chunks of the video stream to be viewed by the end-user.
The whole point of broadcasters incorporating RTMP into the streaming setup has evolved widely and is currently referred to as “RTMP Ingest”.
Of course, there are other variants developed by Adobe such as RTMPS, RTMPE, RTMPT, and RTMFP.
What is RTMP Ingest?
An improvised version of the original protocol, RTMP Ingest helps transfer the encoded video content from the encoder to the online video streaming platform owned by the publisher through a sequence of steps.
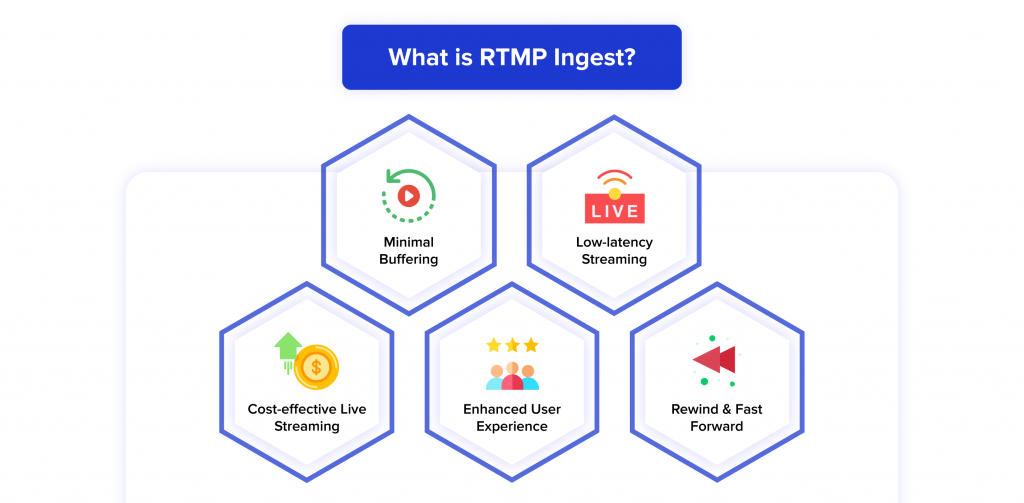
The uses of RTMP Ingest include
- Minimal buffering
- Low-latency streaming
- Cost-effective live streaming
- Enhanced user experience
- Rewind & Fast Forward
Since the workflow demands an RTMP encoder, a low-cost alternative to expensive counterparts available in the market, it is a rather economically feasible option for video distributors across niches.
This is one of the major reasons why RTMP is synonymous with cost-effective live streaming.
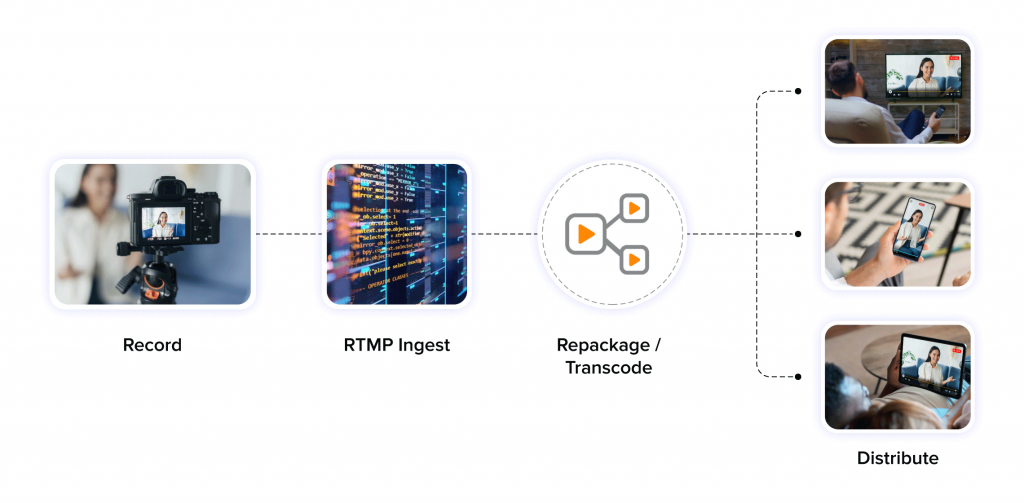
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of How RTMP Ingest Functions
As mentioned before, the transfer of the live encoded video to the online streaming platform involves a series of 3 critical steps as follows.
Handshake —-> Connect —-> Stream
– TCP/ IP Handshake
A reliable connection is established between the client player and the host server through a three-way handshake mechanism.
Three chunks of data between the client and server namely C0, C1, C2 & S0, S1, S2 respectively are transmitted for the session to begin.
Technically, the client incepts the link by sending C0 (protocol version) to the server followed by the second chunk C1 (Timestamp). Now, the server is made to respond to the client request with S0 and S1. And, once the final chunk of data is exchanged between the client and server, a secure RTMP connection is established.
– Connect
During the second phase in the RTMP process, the client and server exchange coded messages using the AMF encoding technique.
AMF (Action Message Format) is an encoding method developed by Adobe Systems and is often used in RTMP typically to signal that the connection is all set to begin live streaming.
– Stream
Now that the RTMP client and server are done with the first two processes (handshake and connection), the RTMP protocol initiates the delivery of real-time video chunks or otherwise called the live streams.
What makes RTMP Ingest different from RTMP?
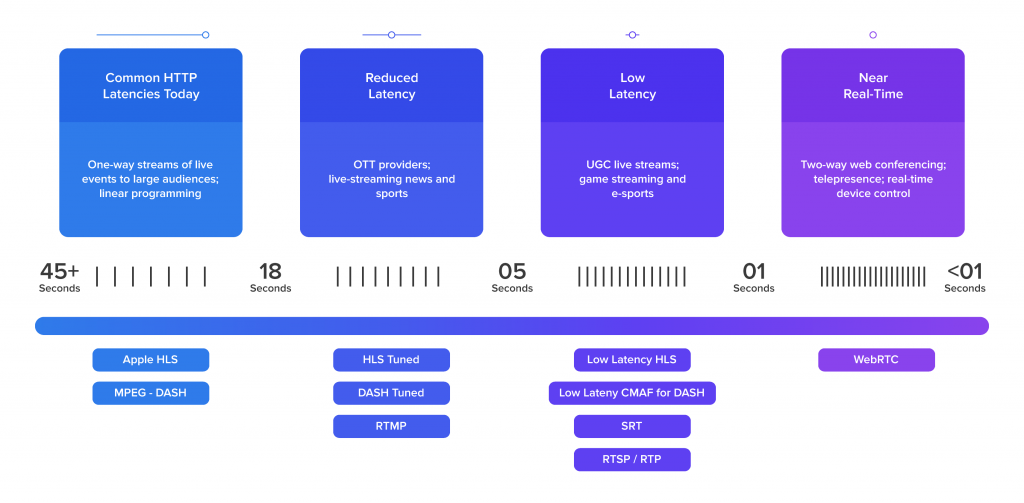
1. RTMP Streaming was originally developed to be compatible with Flash and does not back HTML5 players which is of major use today by several online video platform owners or broadcasters.
Secondly, being unable to support mobile streaming caused RTMP to be less practical in a mobile-first environment.
Moreover, RTMP’s incompatibility with HTTP connections due to the difference in functionality and lower bandwidth issues further complicates live video delivery, urging broadcasters to look past the conventional RTMP.
2. RTMP Ingest, as mentioned earlier, offers easy access to encoders that are highly cost-effective compared to their expensive counterparts.
It is developed to deliver the fastest playback (within a matter of 5 seconds) ensuring reduced buffering, and low latency streaming when combined with HLS (HTTP Live Streaming).
Also, it serves a significant purpose in situations when there comes a need to move your event to a different venue from the one you tested, without having to worry about lag or your CDN (Content Delivery Network) set up.
Recommended Reading
HLS or RTMP: Which Streaming Protocol Should Broadcasters Choose?
Before helping publishers decide which streaming protocol serves best, it is vital to understand what makes the two distinct.
| HLS | RTMP |
| HTTP Live Streaming | Real-Time Messaging Protocol |
| Works on HTTP connection | Works on TCP connection |
| Developed by Apple | Developed by Adobe Systems |
| Compatible with web browsers, smart TV, mobile for both iOS & Android TV app | Not compatible with mobile devices |
| Used extensively by broadcasters | Used in improvised formats |
HLS, as said, is a more popular alternative to RTMP for its compatibility across a wide range of devices and is considered more secure than its predecessor; however, there might be chances of latency in certain applications.

Though the conventional Flash-based RTMP isn’t of much use today, its enhanced version, “RTMP Ingest” is used alongside HLS to deliver buffer-free streams.
Recommended Read: How to stream videos without buffering with HLS protocol?
In other words, the work is split between the two
Initially,
- RTMP Ingest brings the encoded video chunks to the online video hosting platform
- HLS then takes the video streams forward to the supported video player
Hence, it is a coordinated process involving both RTMP and HLS that takes place in the backend to deliver low-latency live streaming.
Though the purpose of RTMP has changed profusely, it is still in use for ingesting and supports HLS in distributing buffer-free real-time streams. However, it is HLS that is widely adopted for its ability to support HTML5 video players and back adaptive bitrate technology (multiple quality streams for different download speeds).
Summing up RTMP Ingest for Live Streaming,
With every passing day, live streaming is becoming increasingly appealing across verticals to cover virtual events, sports broadcasts, online tutorials, and news coverage among others. Even top OTT platforms also prefer it for their seamless content distribution.
As the demand continues to amplify, so is the need for advanced technology to support its growth, giving rise to the innovation of new protocols and fine-tuning of the existing ones.
Once used extensively for on-demand and live video delivery, there are several notions about RTMP being outdated and incompatible with modern-day mobile streaming setups.
But, rather than calling it outdated, it’d be appropriate to state that RTMP’s functionality has shifted in ensuring a smooth transfer of streams from the encoder to the online video hosting platform in the name of RTMP Ingest.
RTMP Ingest now goes hand-in-hand with HLS to distribute high-quality streams to large-scale audiences and will continue to remain of significant importance to broadcasters of the current era.